Tractor, high-power, low-speed traction vehicle and power unit mechanically similar to an automobile or truck but designed for use off the road. The two main types are wheeled, which is the earliest form, and continuous track. Tractors are used in agriculture, construction, road building, etc., in the form of bulldozers, scrapers, and diggers. A notable feature of tractors in many applications is the power-takeoff accessory, used to operate stationary or drawn machinery and implements.
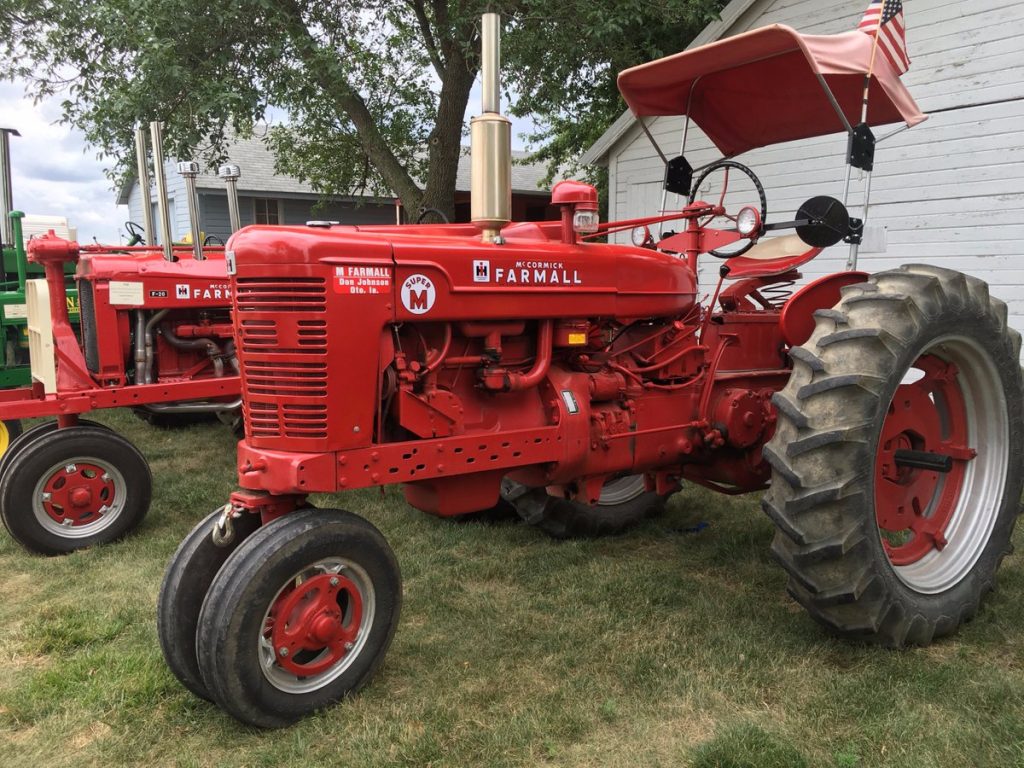

The first tractors, in the sense of powered traction vehicles, grew out of the stationary and portable steam engines operated on farms in the late 19th century and used to haul plows by the 1890s. In 1892 an Iowa blacksmith, John Froehlich, built the first farm vehicle powered by a gasoline engine. The first commercially successful manufacturers were C.W. Hart and C.H. Parr of Charles City, Iowa.
By World War I the tractor was well established, and the U.S. Holt tractor was an inspiration for the tanks built for use in the war by the British and French. Four-wheel-drive tractors can be used under many soil conditions that immobilize two-wheel-drive tractors and caterpillars. Because of their complicated construction and consequent high cost, their use has grown rather slowly.